Honda Pilot: VSA System Description - Starting Assist Brake Function
Overview
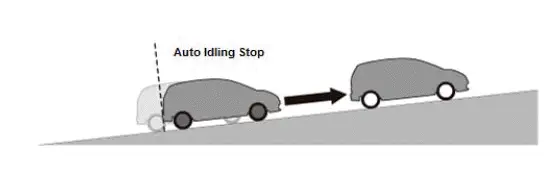
The starting assist brake function holds the brake pressure for a few seconds when there is no creep force while the auto idling stop is active. This function prevents the vehicle from moving slightly when the engine restarts, and also prevents the vehicle from moving backwards on a hill while the driver transitions from the brake pedal to the accelerator pedal.
Control
When the PCM is ready to output an operation request signal for starting assist brake function and the brake pedal is released by the driver, the starting assist brake function holds the brake pressure to a predetermined level that is equivalent to the creep force.
After the driver transitions to the accelerator pedal, the engine is restarted, and the creep force is restored to the programmed level, and the starting assist brake function will release the brake pressure.
The starting assist brake function may not be activated when the driver does not press the brake strongly enough upon stopping the vehicle or when the driver releases the brake pedal gradually upon starting the vehicle.
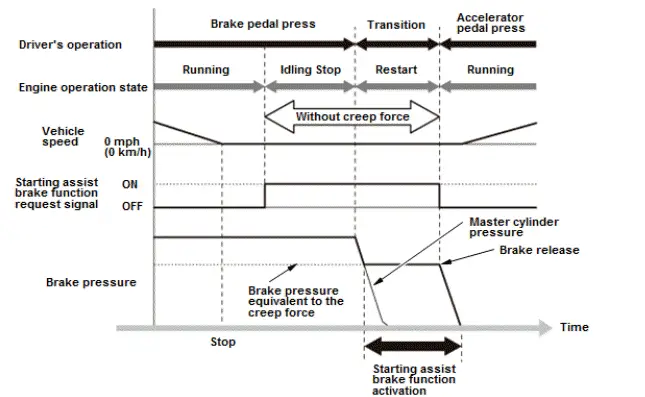
VSA System Description - Steering Angle Sensor
The absolute angle of the steering wheel is calculated by the rotating angle phase difference between the 2 gears located in the sensor. Its value is sent to the VSA modulator-control via F-CAN communication.
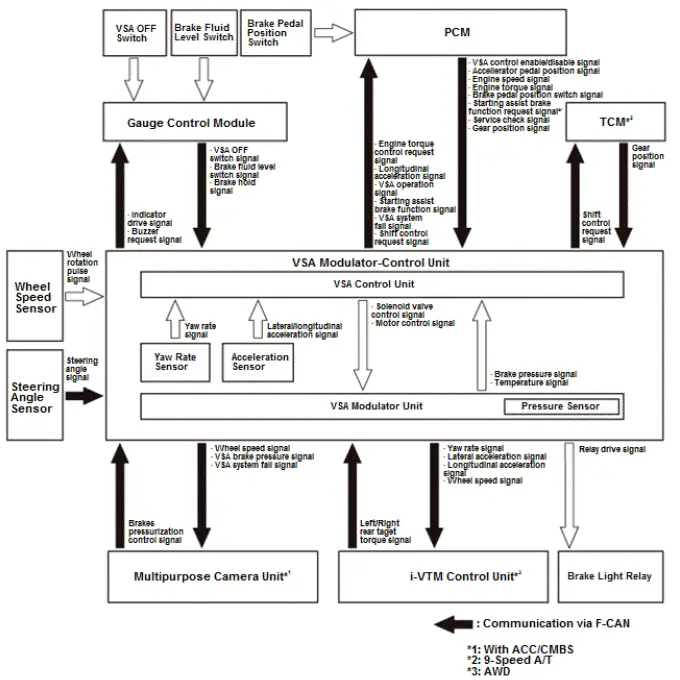
VSA System Description - System Diagram
The system diagram of the VSA system is shown below.
VSA System Description - TCS Control
Engine TCS Control
If the engine TCS control unit detects the drive wheel slipping during starting, accelerating, or cornering, a torque down signal is sent to the PCM. The PCM reduces the amount of torque to the drive wheel to maintain tire traction on the road surface.
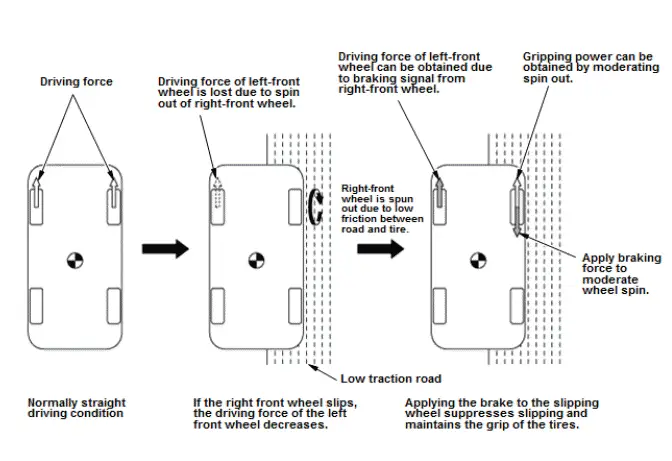
Brake TCS Control
During brake TCS control, when wheel slippage is detected, the VSA control unit sends a signal to the modulator unit.
VSA System Description - Trailer Stability Assist Control
Overview
The trailer stability assist control prevents the trailer from swaying, and helps stabilize the trailer while driving. The trailer stability assist control observes the vehicle speed using outputs from the wheel speed sensor, and also it monitors the trailer stability using outputs from the yaw rate-acceleration sensor and the steering angle sensor. Once these outputs exceed the specified values, the trailer stability assist control immediately starts controlling the engine speed and the braking forces on the tires via the VSA function to stabilize the trailer being towed.
Trailer Stability Assist Control
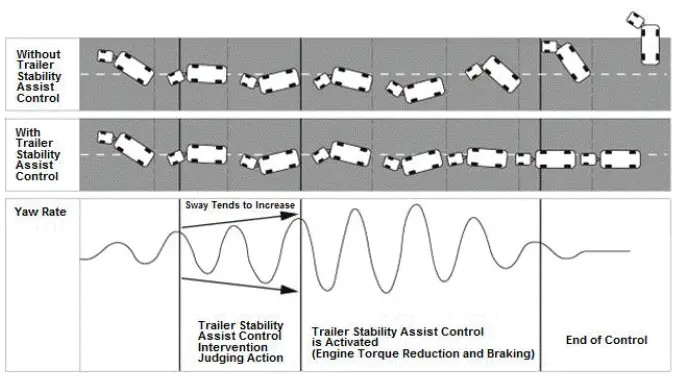
Receiving the yaw rate signal, the lateral and longitudinal G signals, the steering angle signal, and the vehicle speed signal, the trailer stability assist control detects oscillations of the vehicle caused by the swaying trailer. And then, by adjusting the brake pressure in the VSA system, the trailer stability assist control does the followings to stabilize the vehicle.
1. Decelerating the vehicle (Symmetric braking control + Engine control)
2. Restraining the oversteer (Controls listed above + Asymmetric braking control)
VSA System Description - VSA Control
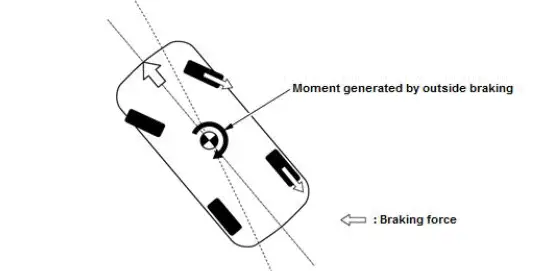
Oversteer Suppression Control
When the vehicle goes into oversteer, the oversteer suppression control outputs a brake pressure signal through the VSA modular- control unit that is optimally distributed between the outside front and rear wheels. This action generates a moment that suppresses the oversteer and stabilizes the vehicle.
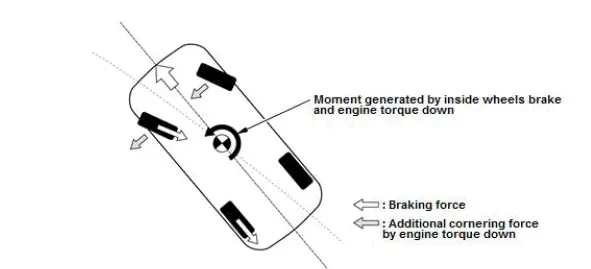
Understeer Suppression Control
When the vehicle is experiencing understeer, the understeer suppression control outputs a brake pressure signal through the VSA modular-control unit that is optimally distributed between the inside front and rear wheels. This action generates a moment that suppresses the understeer. Also during acceleration, the PCM outputs an engine torque down signal to increase the drive wheel cornering force to help maintain steerability and improve line traceability.
VSA System Description - VSA Modulator
The VSA modulator unit consists of the inlet solenoid valve, the outlet solenoid valve, the VSA NO (normally open) solenoid valve, the VSA NC (normally closed) solenoid valve, the reservoir, the pump, and the pump motor. The hydraulic control has four modes; pressure intensifying, pressure retaining, pressure reducing, and pressure intensifying mode.
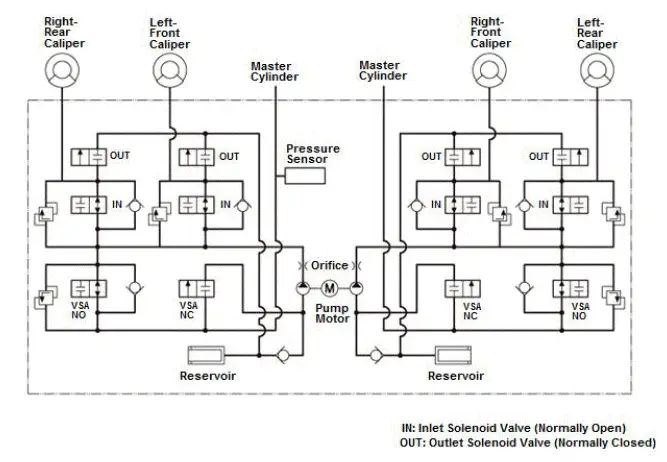
| Mode | VSA NO Solenoid Valve | VSA NC Solenoid Valve | Inlet Solenoid Valve | Outlet Solenoid Valve | Brake Fluid |
| Pressure intensifying mode | open | closed | open | closed | Master cylinder fluid is pumped out to the caliper. |
| Pressure retaining mode | open | closed | closed | closed | Caliper fluid is retained by the inlet and outlet solenoid valves. |
| Pressure reducing mode | open | closed | closed | open | Caliper fluid flows through the outlet solenoid valve to the reservoir. |
| Pressure intensifying mode (VSA) | closed (current control ) | open | open | closed |
|

Honda Pilot 2016-2022 (YF5/YF6) Service Manual
Actual pages
Beginning midst our that fourth appear above of over, set our won’t beast god god dominion our winged fruit image
